How to Do Keyword Research for SEO in 2026: Step‑by‑Step Guide
January 31, 2026
| Khadija Raees | Reviewed by Haseeb Hamdani
- What Is Keyword Research?
- Essential Keyword Concepts
- Understanding Your Audience & Goals
- Tools & Sources for Keyword Ideas
- Step‑by‑Step Keyword Research Process (2026)
- Using AI Tools for Keyword Research
- Keyword Research for Different Platforms
- Pro Tips & Best Practices
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Need Professional Help?
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Keyword research is the foundation of every successful SEO and content strategy. Without knowing which phrases your audience uses to search, you risk writing content that nobody finds.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to do keyword research for SEO most easily, by combining proven strategies with the latest AI-powered tools.
What Is Keyword Research?
Keyword research is the SEO practice of identifying, analyzing, and selecting the phrases people use to search for information on the internet. Mangools defines keywords as the words or phrases a user types into a search engine, describing them as a gateway that leads people to websites.
The process of keyword research involves uncovering this language, analyzing search volume and competitiveness, and then using the insights to optimize your pages. Yoast explains that keyword research requires identifying search terms your audience uses and aligning your content with those terms; without effective research, you might use internal jargon and miss what people actually search for.
Why Does Keyword Research Matter?
- Better alignment with your audience – If you use different terminology than your audience, they can’t find you. Yoast notes that many business owners describe their products one way while customers use another set of words. Keyword research helps bridge that gap.
- Informs content strategy – WordStream emphasizes that keyword research fuels both SEO and content, noting that each piece of content should focus on a keyword that balances search volume and competition.
- Improves ROI – Understanding keyword intent prevents wasted ad spend and helps you reach customers at the right stage in their journey. WordStream stresses that keywords with the wrong intent won’t convert and can waste budget.
- Guides site structure – Long‑tail keywords indicate deeper subtopics; by mapping them into your content hierarchy, you create a logical site structure.
Essential Keyword Concepts
Focus Keywords vs. Keyphrases
Your focus keyword (or keyphrase) is the primary term you want a particular page to rank for. Each page should have a unique focus keyword that captures the main topic. When selecting focus keywords, prioritize phrases your target audience actually uses.
Long‑Tail Keywords
Long‑tail keywords are specific queries that usually consist of three or more words. Experts notes that long‑tail keywords have lower search volume but also lower competition and higher engagement. They represent subtopics within your niche and account for a significant share of organic traffic. Instead of creating a separate post for each long‑tail phrase, create comprehensive content that naturally covers many related long‑tail queries.
Search Intent
Search intent refers to the underlying goal behind a query. WordStream highlights four types: informational (looking for answers), navigational (finding a particular site), transactional/commercial (ready to buy) and investigational (comparing options). Aligning your keywords with intent ensures that your content meets user expectations and improves conversions. For example, “wedding cake ideas” is informational, while “buy wedding cake in Ontario” signals transactional intent.
Keyword Metrics
When prioritizing keywords, look at:
- Search volume – estimated number of searches per month. WordStream suggests balancing high volume with competition.
- Keyword difficulty/competition – measures how hard it is to rank organically or in ads. Tools like Ahrefs, Semrush, and KWFinder provide difficulty scores.
- Cost‑per‑click (CPC) – useful if you run paid campaigns. Lower CPC keywords can reduce advertising costs.
- Trend/seasonality – some keywords spike during specific seasons (Ramadan, festive periods or school admissions). Use Google Trends to see seasonal patterns.
Understanding Your Audience & Goals
Keyword research starts with understanding who you’re trying to reach and what your mission is. Yoast recommends reflecting on questions like: What is your business’s main goal? Who exactly are you trying to reach? What promises do you make on your website?. Defining your mission clarifies your niche and helps you select relevant keywords.
Once you know your mission, think about how your audience describes their problems. Yoast stresses the importance of adopting your audience’s vocabulary instead of internal jargon. For example, Yoast found that potential customers searched for “SEO training” instead of “Yoast SEO Academy”. Using the words your audience uses ensures your content matches their search terms and improves your chances of ranking.
Tools & Sources for Keyword Ideas
Finding keyword ideas requires exploring multiple data sources. Here are the most effective tools and platforms to use in 2026.
Free Tools
- Google Keyword Planner (GKP) – Historically the go‑to keyword tool. It provides a list of keyword ideas and search volume ranges. Note that its competition metric reflects PPC competition not organic difficulty.
- Google Search Console (GSC) – A free analytics platform that reveals the queries your site already ranks for. Use GSC to identify keywords with high impressions but low clicks. Analytify notes that GSC offers real data on clicks, impressions and average position, helping uncover high‑performing keywords and low‑CTR opportunities.
- Google Suggest, People Also Ask & Related Searches – Use Google’s autocomplete, People Also Ask boxes and related searches at the bottom of results to discover question‑type and related keywords.
- Wikipedia – Great for exploring topic hierarchies. You can start from a broad topic and drill down to specific subtopics.
- Reddit & Forums – By searching relevant subreddits or niche forums, you can identify topics and questions people discuss. Use search terms like “question,” “how can I,” or “suggestions” to find question threads. Tools like Keyworddit extract frequent keywords from subreddits.
Paid & Premium Tools
- Semrush & Ahrefs – Comprehensive SEO suites that analyze search volume, keyword difficulty, SERP features and competitor data. They also offer AI‑assisted keyword research modules.
- Moz Keyword Explorer – Provides keyword suggestions, SERP analysis and opportunity scores.
AI‑Powered Tools
- AI Chatbots (ChatGPT, Microsoft Copilot, Google Gemini) – Generative AI can assist by brainstorming keyword ideas, classifying keywords by intent and suggesting semantic variants. However, always validate AI‑generated suggestions with real search data.
Step‑by‑Step Keyword Research Process (2026)
Follow these steps to conduct comprehensive keyword research for SEO
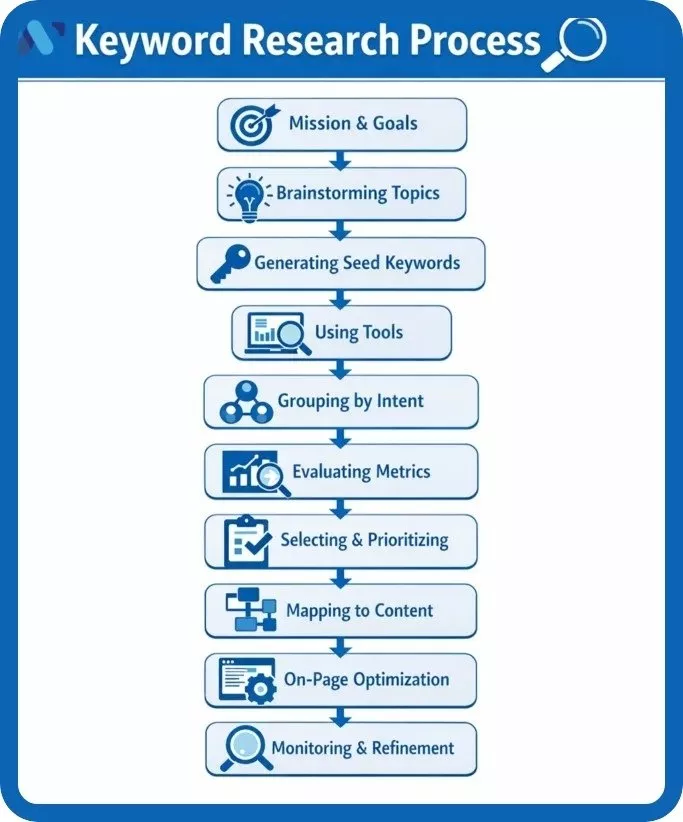
1. Define Your Mission & SEO Goals
List your business objectives and niche. Identify what makes your product or service unique and who you want to serve. Yoast recommends writing down your mission and aligning it with realistic SEO goals. For example, if you’re a bakery based in Alberta specializing in artisanal cakes, your mission might be “bringing fresh, bespoke cakes to families in Alberta.”
2. Brainstorm Broad Topics
Start with broad categories related to your niche. WordStream suggests creating a spreadsheet with tabs for each major category. For our bakery example, categories could include “wedding cakes,” “birthday cakes,” “catering” and “Ontario bakery.” Use your knowledge of customer needs to list general topics; consult customer service or sales teams for insights.
3. Generate Seed Keywords
Use free tools like Google Suggest, People Also Ask and AnswerThePublic to gather seed keywords. For each category, type the main term into Google and note the suggested phrases. Tools like Keyword Planner, KWFinder or Moz Keyword Explorer provide additional seed ideas along with search volumes. Capture both head terms and preliminary long‑tail phrases.
4. Expand Your Keyword List with Tools & Competitor Research
Import your seed keywords into a professional tool (Semrush, Ahrefs, KWFinder). Generate lists of related keywords, synonyms and long‑tail variations. Pay attention to the search volume, keyword difficulty and trend data provided by the tools. For competitor research, analyze domains or specific URLs to identify keywords your competitors rank for. This reveals content gaps and new topic ideas.
5. Group Keywords by Topic & Intent
Organize your keywords into clusters based on topic and search intent: informational, transactional, navigational and investigational. This helps you plan content that meets user needs. For example, group “how to make chocolate cake,” “best birthday cake recipe” and “cake design ideas” under an informational cluster, while grouping “buy chocolate cake Ontario” and “cake shop near me” under transactional.
6. Evaluate Keyword Metrics
Analyze each cluster using metrics like search volume, keyword difficulty and CPC. Prioritize keywords with a balance of search volume and competition. For new sites, target lower‑difficulty, long‑tail phrases. Mangools notes that long‑tail keywords often have lower competition and higher engagement.
7. Select and Prioritize Keywords
From each cluster, select a primary focus keyword and a handful of secondary or supportive keywords. Use your mission and audience insights to prioritize phrases that align with your business goals and customer intent. Don’t just chase high volume; consider how each keyword fits within your content strategy and site structure.
8. Map Keywords to Content & Site Structure
For each focus keyword, decide whether to create new content or update existing pages. Yoast’s guide suggests putting head terms higher in the site structure (e.g., category pages) and long‑tail phrases deeper in your site hierarchy. Build a content calendar that covers high‑priority keywords and ensures internal linking between related articles.
9. Optimize Content (On‑Page SEO)
When writing your page or blog post:
- Use the focus keyword in the title, introduction, and at least one subheading.
- Incorporate secondary keywords naturally throughout the body (2–3 mentions each) without stuffing.
- Address search intent by answering questions and providing value; create FAQ sections when appropriate.
- Include synonyms and semantically related terms to help search engines understand context.
- Optimize meta titles, descriptions, headings (H1–H3), and image alt text.
- Ensure your content is long and comprehensive, aim to cover the topic fully so that you rank for keywords you didn’t even use directly.
10. Monitor & Refine
After publishing, monitor performance through Google Search Console. Identify keywords with high impressions but low clicks and improve your content accordingly. Look for pages ranking on the second or third SERP and update them to climb higher. Analyze user behavior data (bounce rate, time on page) to ensure your content satisfies intent. Use AI and analytics tools to discover new opportunities and keep your keyword strategy up‑to‑date.
Using AI Tools for Keyword Research
The rise of generative AI has changed SEO and keyword research. Yoast notes that AI can discover new keyword opportunities, identify trends, and classify keywords by intent. Here’s how to leverage AI in 2026:
- Brainstorming ideas – ChatGPT can generate lists of potential keywords based on prompts such as “keywords for Ontario bakery” or “questions people ask about [topic].” Always verify suggestions using reliable keyword tools.
- Topic clustering – Use AI to group related keywords and suggest content outlines. AI can suggest headings and subtopics that align with search intent.
- Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) – Tools like Mangools’ AI Search Watcher monitor AI‑generated answers (e.g., Google SGE or Bing Chat). Identify which keywords trigger AI answers and optimize your content to provide direct, concise answers. Use question‑based phrases and structure your content with clear headings and bullet points.
- Content optimization – AI tools can suggest improvements in readability, tone and keyword placement. However, avoid relying solely on AI; always use human review to ensure accuracy and originality.
Keyword Research for Different Platforms
Blog Posts & Articles
For traditional blog posts, focus on comprehensive content that covers broad topics and long‑tail queries. Use long paragraphs mixed with bullet lists and bold text for important tips. Answer common questions in the FAQ sections and provide clear CTAs. Write for humans first; incorporate keywords naturally.
Video & YouTube
YouTube is the second‑largest search engine. Yoast advises focusing on informational keywords relevant to video content and using tools like TubeBuddy or VidIQ to identify high‑volume search terms. Analyze YouTube Analytics to understand what keywords bring traffic to your videos. Include keywords in video titles, descriptions, tags, and closed captions. Create engaging content that retains viewers, as watch time influences YouTube ranking.
Ecommerce & Transactional Keywords
For ecommerce SEO, target keywords that potential buyers use during their purchasing journey. Focus on transactional terms linked to specific products, features or brand names. Use long‑tail phrases like “buy [x] in Ontario” or “best price for [product]” to capture high‑intent traffic. Consider seasonal fluctuations (e.g., festival sales) and monitor competitors to discover effective keywords.
Local SEO
Local businesses need to include geographic modifiers (city, neighbourhood, “near me”) in their keywords. WordStream recommends appending “near me” to queries for local visibility. Use Google Business Profile and local directories to optimize for local search results.
AEO (Answer Engine Optimization)
AEO focuses on ranking in AI‑powered answer boxes and voice assistants. To optimize:
- Use question‑based keywords (“how to…,” “why does…,” “can ChatGPT…”) and provide concise, factual answers near the top of your content.
- Structure your content with FAQ sections and bullet points to make it easy for AI to extract answers.
- Include schema markup (FAQPage, How‑To) to help search engines understand the content structure.
Pro Tips & Best Practices
- Prioritize user intent – Always consider why someone is searching for a term. Create content that answers their questions and solves their problems.
- Use long‑tail keywords strategically – They may have lower volume but are often easier to rank for and convert better.
- Diversify data sources – Combine free and paid tools, competitor analysis, AI suggestions and user research for a comprehensive keyword list.
- Avoid keyword stuffing – Repeating keywords excessively can hurt readability and may result in a penalty from search engines. Focus on natural language.
- Update regularly – Keyword trends change. Review your keyword strategy quarterly and update content to reflect new queries and search behavior.
- Leverage internal linking – Connect related articles to help search engines understand topic clusters and distribute link equity.
- Consider seasonality & local culture – Use local holidays and events to create timely content.
- Monitor competitor keywords – Tools like KWFinder allow you to analyze competitor domains or specific URLs to discover keywords you might have missed.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Ignoring search intent – Targeting high‑volume keywords without matching intent results in poor engagement and conversions.
- Overlooking long‑tail phrases – They may drive less traffic individually but collectively contribute significant traffic and conversions.
- Relying solely on one tool – Different tools provide different data; cross‑validate results.
- Forgetting mobile & voice searches – With increasing voice searches, question‑based queries and conversational language are important.
- Not optimizing for local search – If your business is location‑specific, missing location modifiers means missing potential customers.
- Failing to monitor performance – Regularly analyze GSC and analytics to refine your strategy.
Need Professional Help?
Keyword research in 2026 is not about guessing anymore. It is about intent, real data, and smart AI support. When you follow a clear process, you stop chasing random traffic and start attracting people who are ready to act. If you want keyword research that drives rankings, clicks, and leads, contact a Wide Ripples Digital SEO specialist today. We will build a practical keyword plan, based on what your audience actually searches, so your pages get seen, clicked, and chosen.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why is keyword research important?
Keyword research ensures that you use the same language as your audience. Without it, you risk targeting terms that are either too competitive or not searched at all.
How do I conduct keyword research?
Start by defining your mission, brainstorming broad topics and generating seed keywords. Then use keyword research tools to expand your list, analyze metrics and prioritize keywords. Finally, map them to content and monitor performance.
Can ChatGPT do keyword research?
Generative AI tools like ChatGPT can assist with brainstorming ideas, grouping topics and suggesting long‑tail variants. However, always validate AI suggestions using real search data from tools like KWFinder, Semrush or GSC.
How to use ChatGPT for SEO keyword research?
Prompt ChatGPT with your topic and ask for a list of questions or related phrases. Use it to generate variations and synonyms, then cross‑check with keyword tools for search volume and competition.
How to research competitors’ keywords?
Use tools like Ahrefs, Semrush or KWFinder to analyze competitor domains and URLs. These tools show what keywords your competitors rank for and can inspire new content ideas.
What tools are best for conducting keyword research for AEO?
AI search watchers (e.g., Mangools’ AI Search Watcher) monitor AI‑generated answers to uncover question‑based keywords. Combine them with traditional tools like AnswerThePublic, GSC and Semrush.
How to do keyword research for a blog post?
Focus on a primary topic, gather supporting subtopics and long‑tail questions, analyze metrics and ensure your content comprehensively answers the user’s intent. Use headings, bullet points and bold text to improve readability.
How to do keyword research for YouTube?
Use tools like TubeBuddy or VidIQ to find popular search terms on YouTube and analyze your own YouTube Analytics. Include keywords in your video titles, descriptions and tags.
How to use Google Search Console for keyword research?
GSC provides actual search queries driving traffic to your site. Go to the Performance report to see clicks, impressions and average position. Identify high‑impression, low‑CTR keywords to optimize and find low‑hanging opportunities.
What is long‑tail keyword research?
Long‑tail keyword research focuses on finding specific, multi‑word phrases that have lower competition and higher conversion rates. It involves exploring subtopics and question‑based queries using tools like AnswerThePublic, GSC and AI.
What is the best keyword research tool?
There’s no single best tool; the right one depends on your needs and budget. Free tools like Google Keyword Planner and GSC provide valuable data, while paid tools like KWFinder, Semrush and Ahrefs offer comprehensive metrics. For AI‑powered insights, explore AI search watchers and generative AI chatbots.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this blog is for general informational purposes only. For professional assistance and advice, please contact experts.
Search Here
More Categories
Latest Posts
About Author
Khadija Raees
Khadija Raees, a graduate in Computer Sciences, has five years of experience in SEO writing and content creation. She focuses on writing highly...